
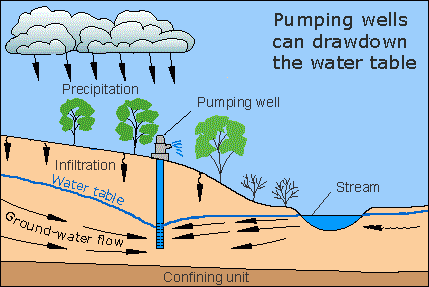
Net implementation costs is US$17.4 billion. From nine data points covering Europe, North America, and Asia, the installation cost is US$33402 per million cubic meters of water saved. Leakage activities were estimated (over 18 data points) to reduce this by 29 percent, and emissions factors for this grid electricity came from the guides of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).įirst costs for pressure management and active leak control were averaged based on how much water they save on average, so are reported here in million cubic meters of water saved. The result was 1.27 gigawatt-hours of electricity per million cubic meters of water supplied. Scenario 2: This linear growth reaches 47 percent of the global water distribution network.Įmissions estimates were calculated for electricity consumption for water treatment and distribution (with a weighted share for each of desalination, surface water, and ground water).Scenario 1: The adoption of pressure management and active leak control is assumed to rise linearly to 38 percent of the global water distribution network.These were assessed in comparison with a Reference Scenario, in which the solution’s market share was fixed at the current levels. Impacts of increased adoption of water distribution from 2020 to 2050 were generated based on two growth scenarios. Relying on both recently reported data and theoretical estimates over several years and studies strengthened the final estimate used: 438 billion cubic meters of water treated and supplied in 2014. Combined with water supply statistics from the World Health Organization and United Nations Children's Fund (WHO/UNICEF, 2015) to arrive at Urban and Rural shares, the total addressable market for each region was obtained. This estimate was combined with empirical data reported by hundreds of water utilities in the International Benchmark Network Database (IB-NET, n.d.) to arrive at estimates for per-capita water production for all regions in the world. An exponential curve of water use per year was developed from 20 previous estimates of global water distribution for specific years dating from 1900 to 2025 (Hejazi et al, 2013). Project Drawdown’s method starts by estimating how much water is actually used globally by municipalities. This analysis examines the financial and emissions impacts of a high adoption of pressure management and active leak control globally, and compares that to conventional system management with no specific leak detection program. Prices and precision vary for these approaches, but the value can be high, especially for high operating cost, high water scarcity regions. Active leak detection can be performed using a range of technologies, such as thermal imaging, noise logging, or gas injection. Pressure management involves installing pressure valves at water inlets and outlets to better monitor the flow of water and pressures, and leads to reductions in pipe bursts and leaks from broken pipes. Pressure management and active leak detection are two major ones. There are a number of ways to minimize leakage. Saving just half of these losses would supply water to an additional 100 million people (The World Bank, 2006). This has a direct impact on the production cost of water, as well as on the available quantity of potable water. However, a significant amount of water is lost in the distribution network (e.g., by pipe leakage, meter error, and unauthorized consumption): the global average loss is estimated at 35 percent. Up to 80 percent of that energy is used for pumping alone. Water utilities are among the biggest consumers of electricity globally, corresponding to about 1 percent of total electricity use in the world.
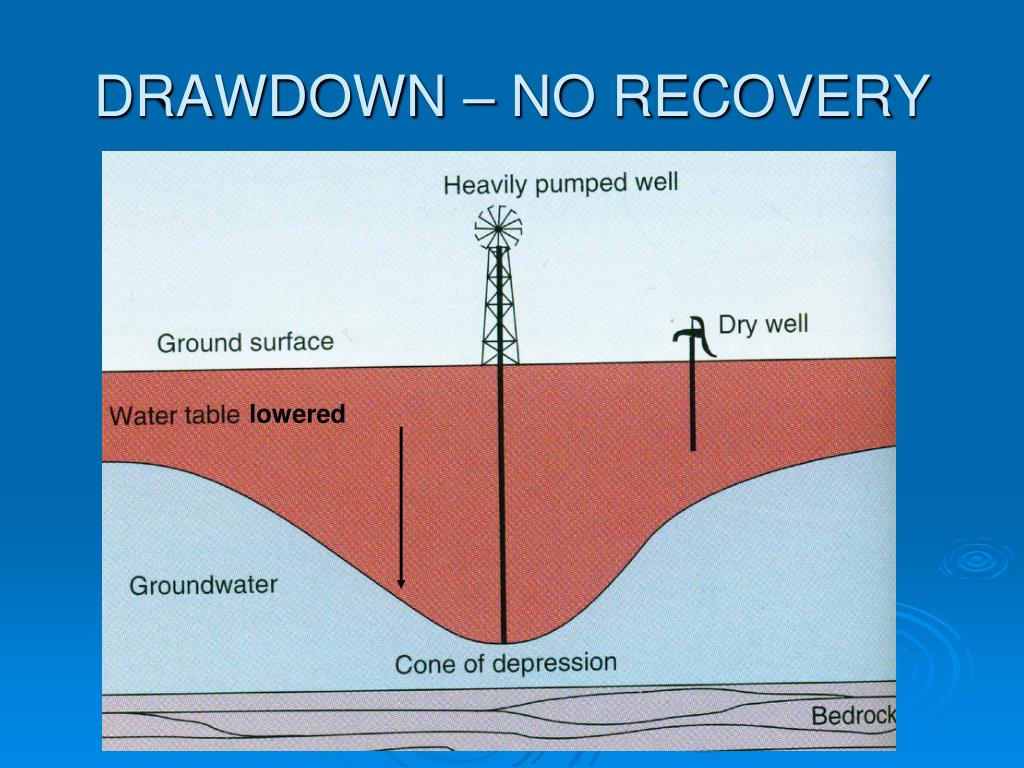
This solution replaces conventional water system management with no specific leak detection program. Project Drawdown defines water distribution as reducing water leakage or oversupply of regional water, which reduces pumping and pressurization electricity and associated greenhouse gas emissions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
